Imagine you’re in a bustling workshop, staring at a broken machine part that’s halting your entire production line. You’ve got deadlines looming, and the traditional way to fix it means waiting weeks for a new mold to be crafted by hand. Frustrating, right? That’s the story of countless manufacturers before repmold changed the game. As someone who’s dived deep into modern manufacturing trends, I’ve seen how this innovation turns headaches into high-fives. Picture this: a small startup I know was on the brink of missing a major client order because of a faulty prototype mold. They switched to repmold, and in just days, they had precise replicas ready, saving their deal and boosting their reputation. You might be thinking, “Could this work for me?” Absolutely. If you’re tired of slow, costly mold-making that wastes materials and time, repmold is your ticket to efficiency. It’s not just a tool, it’s a lifeline for anyone in production, from hobbyists to industry giants. In this post, you’ll discover how repmold can slash your costs, speed up your workflow, and make your operations greener. Let’s dive in and see how it can transform your projects.
Repmold, short for replication molding, is a cutting-edge technique that lets you create accurate molds by copying shapes using digital tools and additive manufacturing. Why does it matter? In today’s fast-paced world, where customization and quick turnaround are key, repmold cuts down on waste, reduces costs, and boosts precision. You’ll learn the ins and outs: from how it works to real-world applications, plus tips to get started. Repmold combines rapid prototyping with sustainable mold making, making it ideal for precision manufacturing and digital molding processes. Think of it as the bridge between idea and product, using additive manufacturing molds to replicate designs flawlessly. Whether you’re exploring replication molding for the first time or looking to optimize your setup, this guide packs the insights you need.
Understanding Repmold: The Basics of Replication Molding
Repmold starts with a simple yet powerful idea: replicate instead of recreate. You design a part digitally, print a master model, then form a mold around it for quick copies. This process integrates 3D printing, CNC machining, and AI optimization for results that are fast and spot-on.
How the Repmold Process Works Step by Step
- Design Phase: Use CAD software to craft your model. Scan existing parts if needed.
- Master Creation: 3D print the initial prototype.
- Mold Formation: Apply materials like silicone or resin over the master.
- Replication: Fill the mold with your chosen substance.
- Finishing Touches: Cure, clean, and test for quality.
This sequence can wrap up in hours or days, unlike traditional methods that drag on for weeks. Bold move: always simulate digitally first to catch issues early.
Why Repmold Stands Out in Precision Manufacturing
Traditional molding often leads to errors from manual work, but repmold’s digital foundation ensures consistency. For example, in optics, replication achieves surfaces as smooth as 5 Angstroms. Pros include lower costs and scalability; cons might be initial setup learning curve. As I’ve experimented with similar tech, repmold feels like having a super-efficient assistant.
Rhetorical question: Ever wondered why big companies like those in aerospace swear by it? It’s the speed. Stats show up to 50% reduction in production time. Relate it to everyday life: just like copying a key at the hardware store, but for complex parts.
Sources back this up. A study on hydrogel-assisted molding highlights precise replication for tissue engineering, reducing toxicity and enabling complex shapes. Nanoscribe’s work shows submicron features in mass production via injection molding. Newport details epoxy replication for optics, compensating for imperfections. Elveflow explains PDMS soft lithography for microfluidics. Harvard’s research on polymeric replica molding pushes nanomanufacturing.
Transitioning smoothly, now that you grasp the basics, let’s explore the perks that make repmold a must-have.
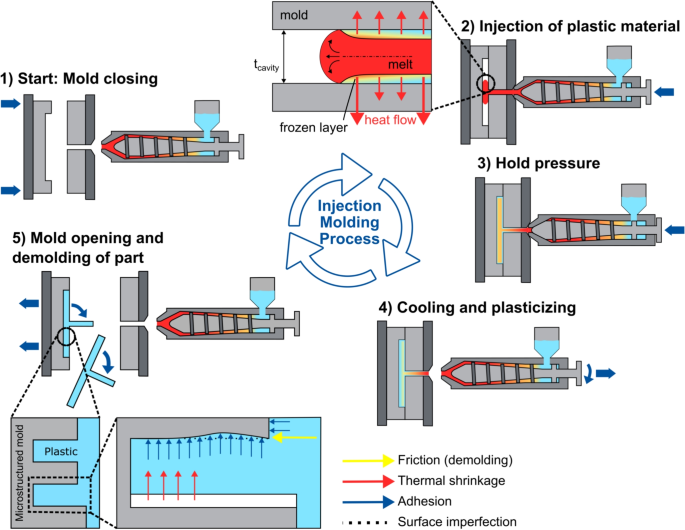
Source: link.springer.com
Manufacturing of micro-structured PVD hard coated molds and their …
The Top Benefits of Repmold for Modern Manufacturers
Repmold isn’t just faster; it’s smarter. It slashes lead times by up to 60%, cuts costs in half, and promotes eco-friendly practices.
Speed and Efficiency Gains
Forget waiting months. Repmold delivers molds in days, thanks to digital integration. A mid-sized auto firm saw 50% time cuts. Tip: Pair with simulation software for even quicker iterations.
Cost Savings and Waste Reduction
Less material waste means big savings. Sustainable mold making aligns with green goals, reducing scrap by 35% in some cases. Pros: reusable molds; cons: upfront tool investment.
Precision and Quality Assurance
Achieve nanometer accuracy. In medical devices, this ensures compliance. Humor: It’s like photocopying a masterpiece without smudges.
Sustainability in Action
Uses eco-materials, lowers energy use. Relate: Like recycling but for manufacturing.
Flexibility for Customization
Easy design tweaks. Examples: custom electronics casings.
Data from sources: TDS Magazine notes cost-effectiveness and scalability. Bright Magazine highlights efficiency in low-volume production. Atalys praises injection molding for medical precision. Stensborg compares RNIL for surface replication. Wiley study shows high replication quality in polymers.
With these benefits in mind, see how repmold applies across sectors.
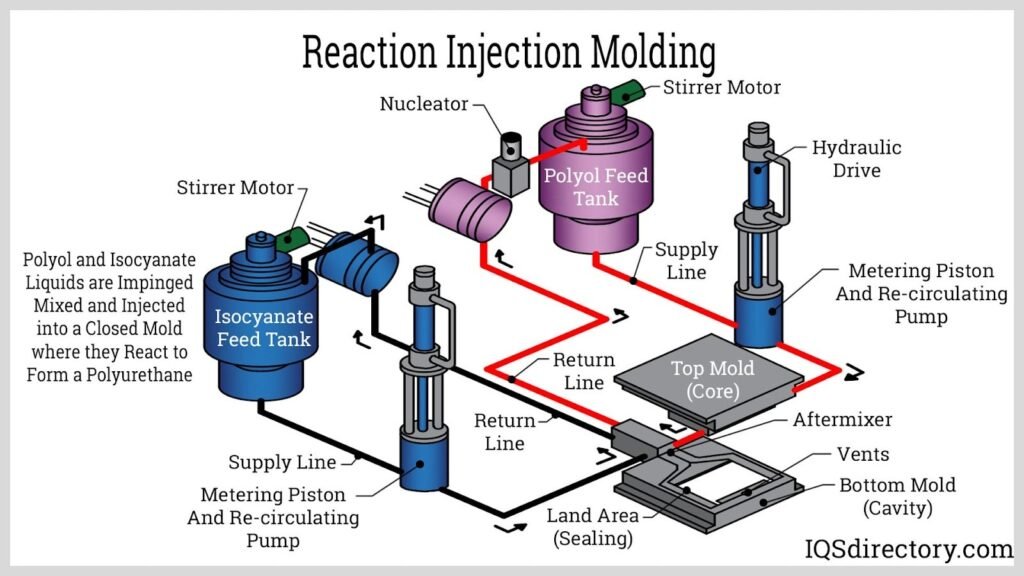
Source: iqsdirectory.com
RIM Molding | Reaction Injection Molding Process & Uses
Repmold Applications: From Automotive to Medical Devices
Repmold shines in diverse fields, enabling innovation where precision counts.
Automotive Industry Uses
Prototyping engine parts quickly. Example: 50% cost drop for dashboards.
Aerospace and High-Performance Parts
Lightweight molds for extreme conditions.
Medical and Biotech Innovations
Prosthetics, microfluidics. HASTE method replicates for tissue design.
Consumer Electronics and Products
Custom casings. Tip: Use for small-batch testing.
Education and Research
Hands-on learning. Pros: accessible; cons: scale limits.
Stats: Startups iterate three times faster. Sources: NTA Testing lists applications. AndreaClined64 provides case studies. Nanoscribe for microoptics. Nature on metal molds. Roctool for surface replication.
Next, compare it to old-school methods.
Repmold vs. Traditional Mold-Making: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Traditional methods rely on manual crafting, while repmold digitizes everything.
Time and Cost Breakdown
| Aspect | Traditional | Repmold |
| Time | Weeks-Months | Days |
| Cost | High labor | 35% lower |
| Waste | High | Low |
Quality and Scalability Differences
Repmold offers better consistency.
When to Choose Each
Use traditional for massive volumes; repmold for flexibility.
Examples: Furniture restoration uses silicone molds. Tip: Hybrid approaches work best.
Sources: DailyFactBehind on cost efficiency. McByMaricruz on time reduction. ElfMalls on lead times. VistaNews on prototyping changes. VersatileMD on compression molds.
Ready to try? Here’s how.
Practical Tips for Getting Started with Repmold
Start small, scale up.
Essential Tools and Materials
- CAD software
- 3D printer
- Silicone, epoxy
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Don’t skip simulations.
Advanced Techniques
Integrate AI for optimization.
Pros/cons: Easy entry, but learn curves.
Sources: HopesTech on how it works. ParkwayDome on future. IdiomsInsider explanations. KnowingImagination on shift. GreatAmericanRealty on precision.
Looking ahead.
The Future of Repmold: Emerging Trends and Innovations
AI and new materials will push boundaries.
Integration with AI and Automation
Predictive designs.
Sustainable Advances
Bio-based resins.
Potential Challenges
Adoption barriers.
Stats: Market growth projected high.
Sources: ChloeMullaney on benefits. FinancialAuditCPA on applications. Mechomo on 3D printing. YouTube on PDMS bonding. Harvard on 3D molding.
FAQs
What is repmold?
Replication molding using digital and additive tech for fast molds.
How does repmold differ from injection molding?
It’s quicker for prototypes, while injection suits mass production.
Is repmold suitable for beginners?
Yes, with basic tools.
What materials work with repmold?
Silicone, resins, polymers.
How much does repmold save on costs?
Up to 35-60%.
Can repmold be used for large-scale production?
Yes, with scaling.
What industries benefit most from repmold?
Automotive, medical, electronics.
Are there environmental benefits to repmold?
Absolutely, less waste and energy.
Repmold revolutionizes manufacturing by offering speed, precision, and sustainability. Key takeaways:
- Cuts production time dramatically.
- Reduces costs and waste.
- Enables high-quality, custom parts.
- Supports diverse industries.
- Promotes green practices.
Embrace repmold to stay competitive. Share your repmold experiences in the comments, or try it out and tell me how it goes!

